3G is the third generation of mobile phone standards and technology, superseding 2.5G, and preceding4G. It is based on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) family of standards under the International Mobile Telecommunications programme, IMT-2000.
3G networks enable network operators to offer users a wider range of more advanced services while achieving greater network capacity through improved spectral efficiency. Services include wide-area wireless voice telephony, video calls, and broadband wireless data, all in a mobile environment. Additional features also include HSPA(High Speed Packet Access) data transmission capabilities able to deliver speeds up to 14.4Mbit/s on the downlinkand 5.8Mbit/s on the uplink.
Unlike IEEE 802.11 (common names Wi-Fi or WLAN) networks, 3G networks are wide area cellular telephone networks which evolved to incorporate high-speed internet access and video telephony. IEEE 802.11 networks are short range, high-bandwidth networks primarily developed for data.
REVOLUTION FROM 2g TO 3g
Speed
3G service may not be able to point to a standard and say that the speeds it specifies are not being met. While stating in commentary that "it is expected that IMT-2000 will provide higher transmission rates: a minimum speed of 2Mbit/s for stationary or walking users, and 348 [sic] kbit/s in a moving vehicle,"[1] the ITU does not actually clearly specify minimum or average speeds or what modes of the interfaces qualify as 3G, so various speeds are sold as 3G intended to meet customers expectations of broadband speed. It is often suggested by industry sources that 3G can be expected to provide 384 kbit/s at or below pedestrian speeds, but only 128kbit/s in a moving car.
The 3G network might be divided up in hierarchical fashion:
- Macro cell - the area of largest coverage, e.g., an entire city.
- Micro cell - the area of intermediate coverage, e.g., a city centre.
- Pico cell - the area of smallest coverage, e.g., a "hot spot" in a hotel or airport.

3G Standards
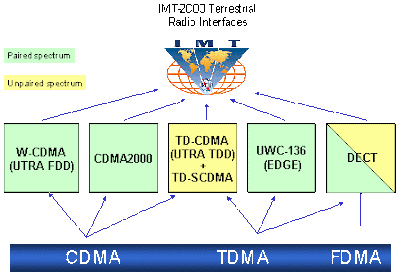
The 3G standard was created by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is called IMT-2000. The aim of IMT-2000 is to harmonize worldwide 3G systems to provide global roaming. However, as was explained in the introduction to this section, harmonizing so many different standards proved extremely difficult. As a result, what we have been left with is five different standards grouped together under the IMT-2000 label:
- W-CDMA
- CDMA2000
- TD-CDMA/TD-SCDMA
- DECT
- UWC-136
At this point, the definition of what is and what isn't "3G" becomes somewhat murky. Of these five standards, only three allow full network coverage over macro cells, micro cells and pico cells and can thus be considered as full 3G solutions: W-CDMA, CDMA2000, and TD-SCDMA. Of the remainder, DECTis used for those cordless phones you have in the house, and could be used for 3G short-range "hot-spots" (hence, it could be considered as being "part of a 3G network"), but it does not allow full network coverage so is not considered further here. And UWC-136 is another name for EDGE which is generally considered to be a 2.5G solution and was considered in the previous section.
So that leaves W-CDMA, CDMA2000, and TD-SCDMA - the bona fide 3G solutions - which will now be covered in more detail:

No comments:
Post a Comment